Anatomy and Pathology related tothe Urinary TractDecember 17, 2012
Mindy M. Horrow, MD, FACR, FSRU, FAIUM
Director of Body Imaging
Einstein Medical Center
Professor of Radiology
Thomas Jefferson School of Medicine
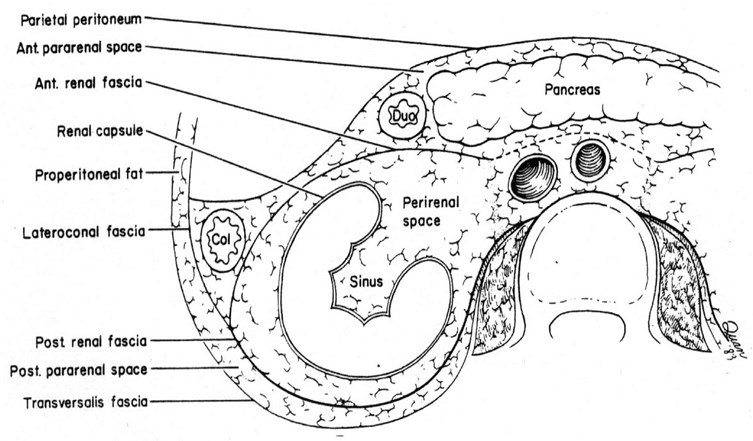
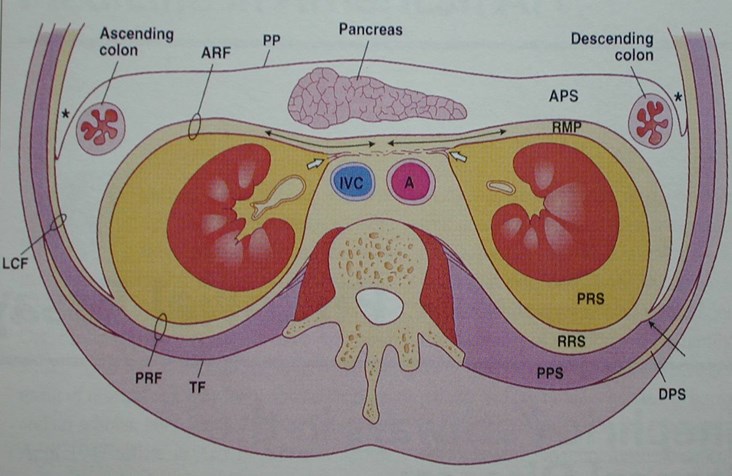
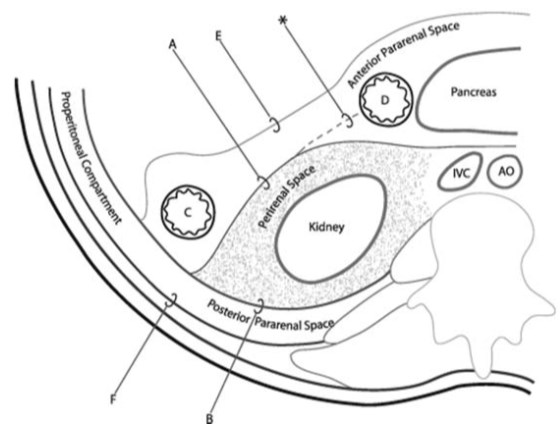
The Retroperitoneal Spaces:
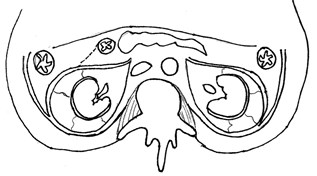

Retroperitoneal compartments
Subcapsular
Perinephric
Anterior Pararenal
Posterior Pararenal
Interfascial

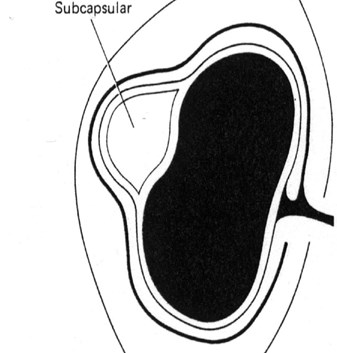
Renal Capsule
Composed of fibroustissue and smoothmuscle
Forms a firm, smoothinvestment for thekidney
Will be sharply deflectedover margin of a sub-capsular collection/masswith flattening andcompression of thekidney

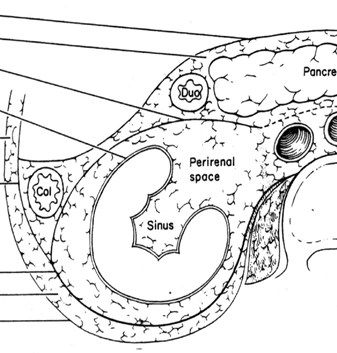
The Perirenal Space
Anterior and post renal fascia
–Gerota’s (anterior) fascia
–Zuckerkandle (posterior) fascia
Extent: Superior, medial,lateral, inferior
Contents

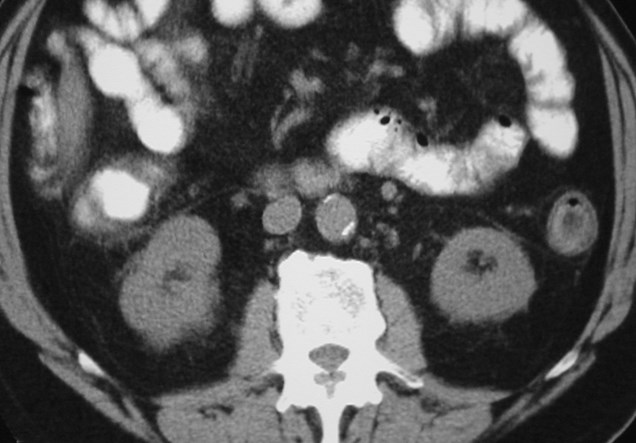
Normal Retroperitoneal Anatomy
Anterior Renal Fascia Posterior Renal Fascia

Extent of Perirenal Space
Superior - open to bare area of liver(and spleen) and contiguous withmediastinum
Medial - above renal hila perirenalspaces are separate, beginning atlevel of hila there is communication
Lateral - ARF, PRF fuse to form lateralconal fascia
Inferior - ARF & PRF converge blendabout 8 cm below kidney

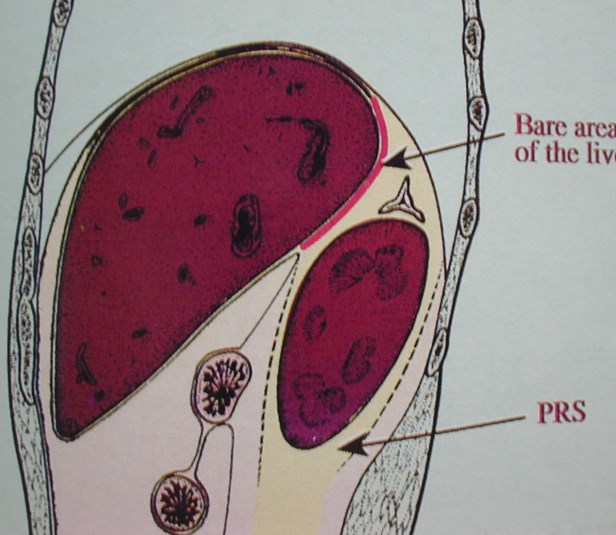

Perirenal space open superiorly to bare area ofliver, closed inferiorly as Gerota’s fascia fuses

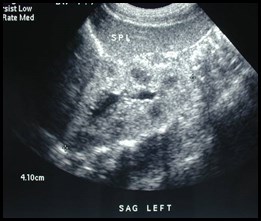
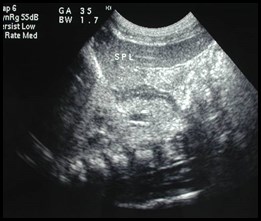
Newborn renal sonogram
Herniation of left kidney and adrenal gland
through Foramen of Bochdalek into posterior mediastinum

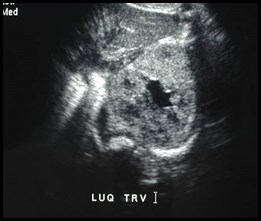
Anatomic variation in lateral conal fasciaallows colon to extend posterior tokidneys: sonographic nightmare!

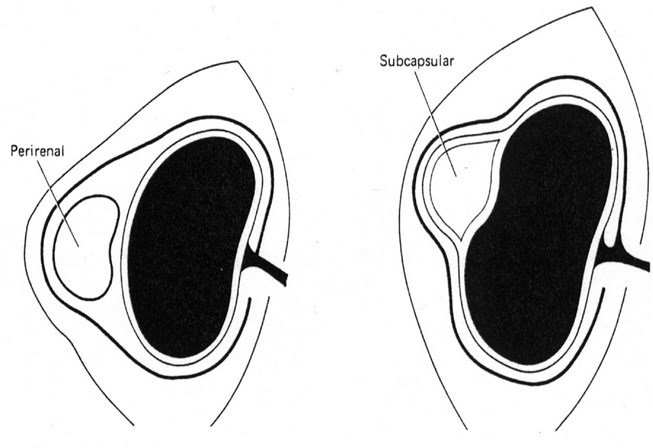
Perirenal collections conform toshape of kidney

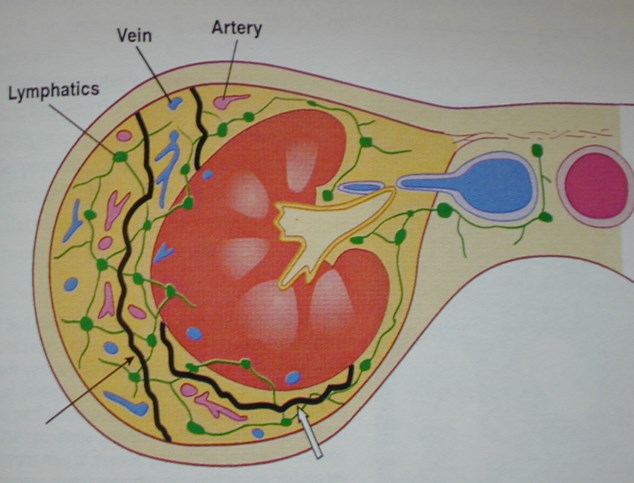
Contents of Perirenal Space
Kidney, proximal collectingsystem, adrenal gland
Renal vasculature and perirenalvessels
Lymphatics
Bridging septa
Variable amounts of fat


Bridging Renal Septa
Fibrous lamellae
3 types:
I -connect renal capsule withrenal fascia
II-only connected to capsule,circumscribing kidney
III-connect ARF to PRF

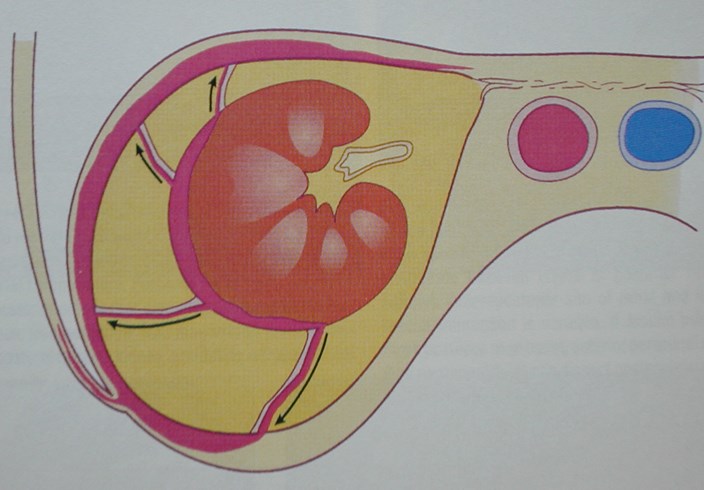
Spread viaPerinephric Bridging Septa
Thickened septa - nonspecific but may beearly sign of renal/perinephric disease
May preclude complete percutaneousdrainage of perinephric fluid collections
Serve as conduit for spread of fluid,inflammation, neoplasm
Involvement of septi depends uponrapidity of process


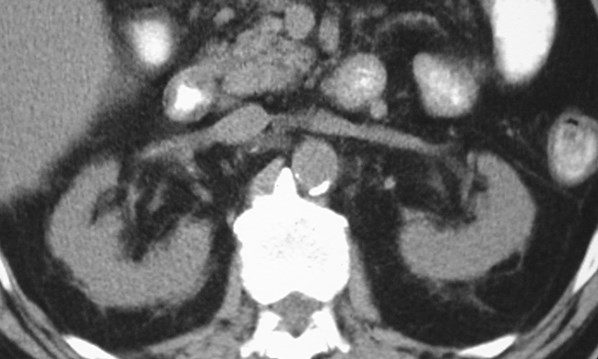
CRF: Prominent bridging septae
and small amount of perinephric fluid

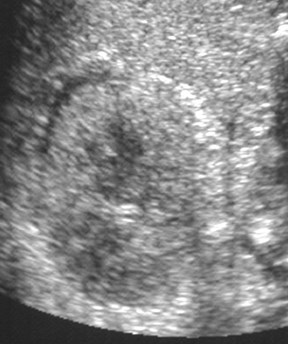
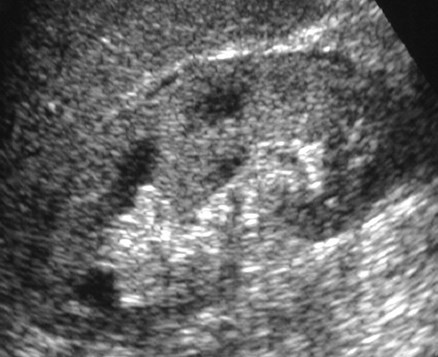
Kidney “sweat sign”
Fluid in perirenal space corresponding tothickened septi and fluid on CT scan
Echogenic kidneys in patient with CRF


Anterior Pararenal Space
Boundaries
–Anteriorly: post parietal peritoneum
–Posteriorly: Gerota’s fascia
Contents: Ascending and descendingcolon, duodenum, pancreas
Continuous across midline, with rootof small bowel mesentery andinferiorly with perirenal, posteriorpararenal and prevesical spaces

Posterior Pararenal Space
Boundaries
–Anteriorly: posterior renal fascia andlateral conal fascia
–Posteriorly: transverse fascia
–Limited by and parallels psoas m.
–Open laterally to flank and inferiorly topelvis
Contents: Fat (no visceral organs)

Interfascial RetroperitonealPlanes
Retromesenteric - between anterior pararenaland perinephric spaces contiguous acrossmidline and laterally with retrorenal and lateralconal space
Retrorenal - between perinephric and posteriorpararenal spaces
Lateral conal
*Combined fascial plane continues into pelvisanterolateral to psoas m. allowing pathway to pelvis
*Trifurcation of 3 planes - anterioposterior location isvariable


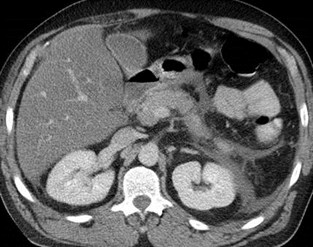
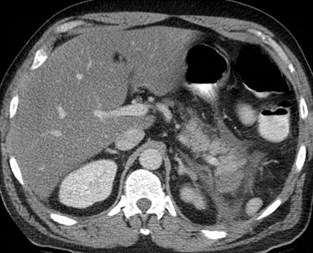
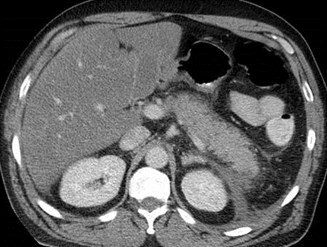
Pancreatitis with fluid in anterior pararenalspace and retromesenteric interfascial space

Pathways of Spread of Diseasein the Retroperitoneum
Slowly accumulating, non-aggressiveprocesses remain confined to 3 mainspaces
Rapidly developing collectionsoverwhelm main spaces, dissecting anddecompressing into adjacent potentialspaces and within fascial planes, acrossbridging septi and through lymphatics

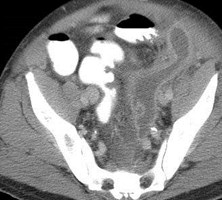
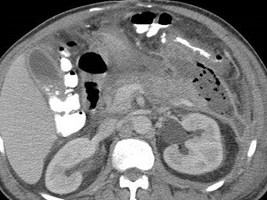
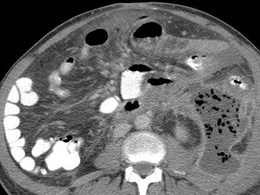
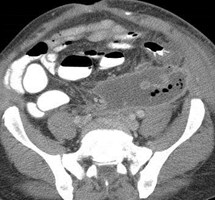
Slow Process:
Infected pancreatic phlegmon in anteriorpararenal space spares perirenal spacespreading to pelvis

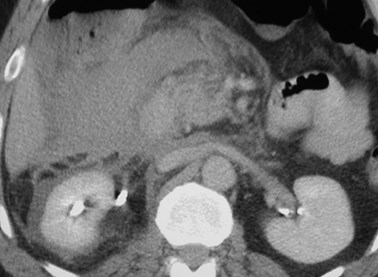
Rapid process:
Acute hemorrhage in anterior pararenal spaceinvolves perirenal space via bridging septi

Lymphatic Spread of Diseasefrom Perinephric Space
Small perirenal lymph nodes
Nodes in renal hilum
Periaortic/pericaval nodes

Lymphatic Spread of Diseaseto Perinephric Space
Transpleural andtransdiaphragmatic lymphaticsfrom lung and mediastinum
to perinephric space

Extension ofRetroperitoneal Fluid into Pelvis
Major route - via fused interfascialplanes with dorsal extension, medialto iliac vessels (perinephriccollections)
Minor route - dorsal extension lateralto iliac vessels in contact withiliopsoas muscle
Minor route - medially into prevesicalspace (anterior pararenal collections)

Inflammatory Processes andFluid Collections
Infections
Pseudocysts
Urinomas
Hematomas
Perforation

Infections
Most originate from kidney
May spread through all spacesand via bare area to peritoneumand thorax

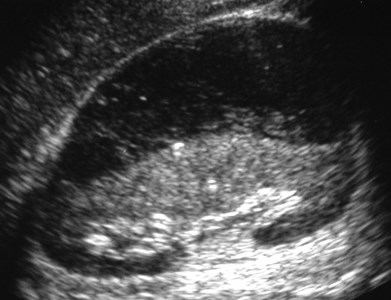
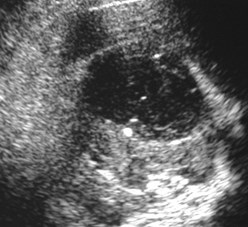
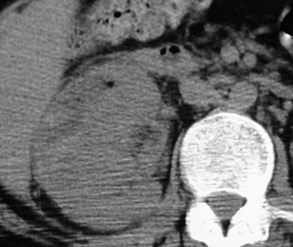
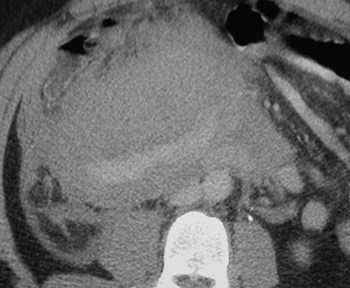
Subcapsular
Abscess

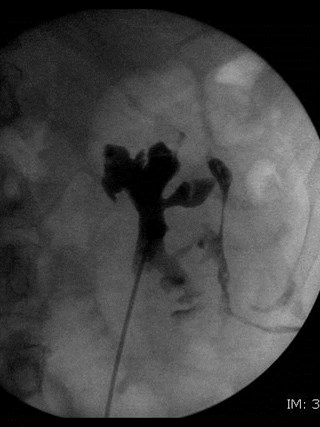
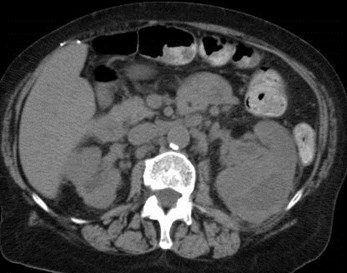
Recurrent urinary tractinfections
Infected subcapsular urinoma

Patient in septic shock- portable abdominal US
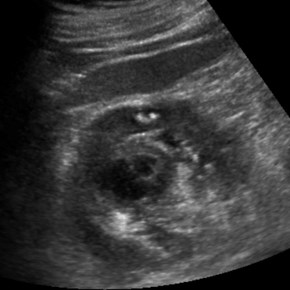
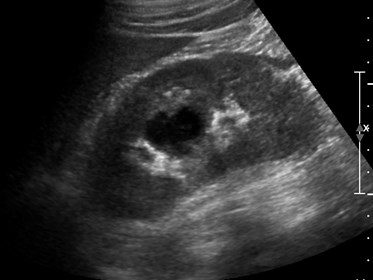
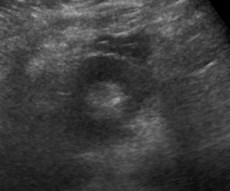

Renal Abscess extending intoperinephric space
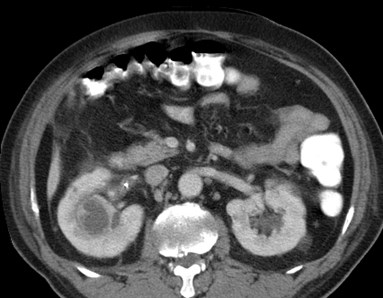
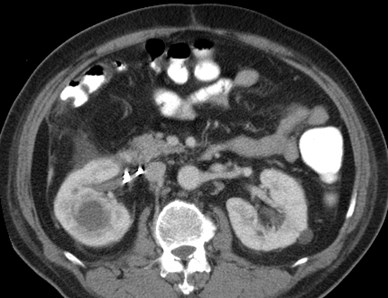

Xanthogranulomatous
Pyelonephritis
Obstructed upper pole Posterior pararenal
and abdominal wall
extension
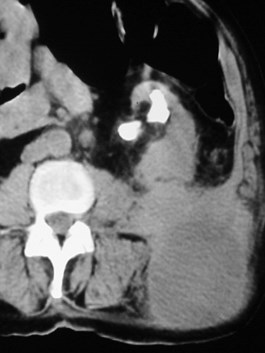
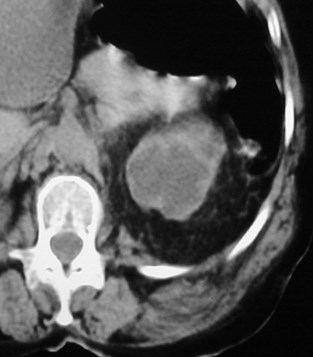

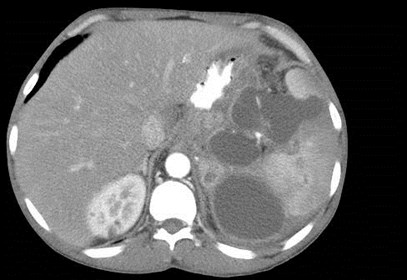
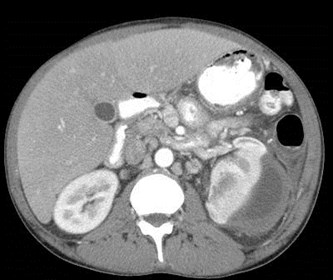
History of Pancreatitis
Subcapsular andperisplenic pseudocysts

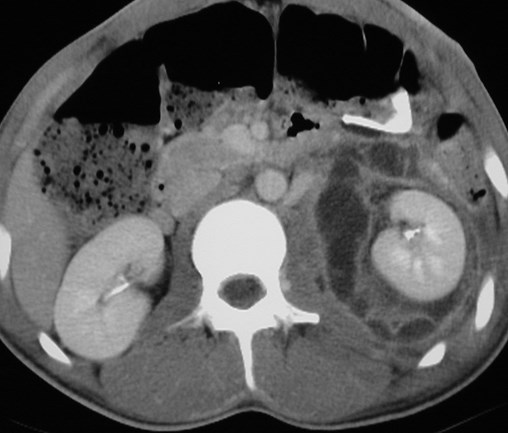
Pseudocyst in perinephric space
Pancreatic Trauma

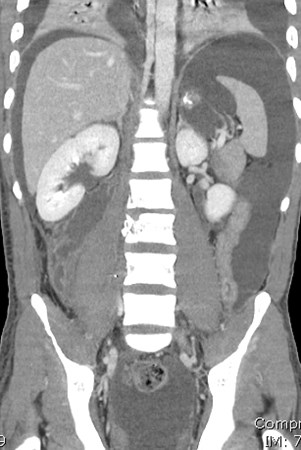
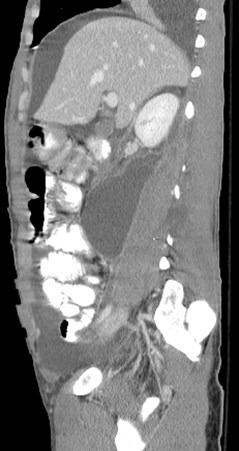
History of gunshot wound to right flank

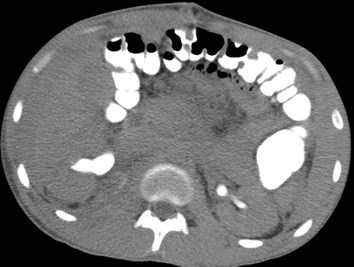
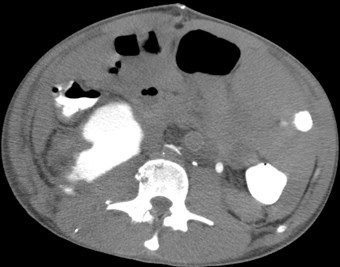
Post Traumatic Perinephric Urinoma

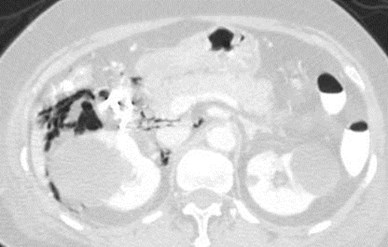
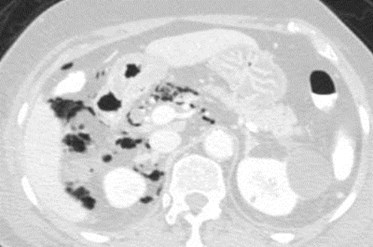
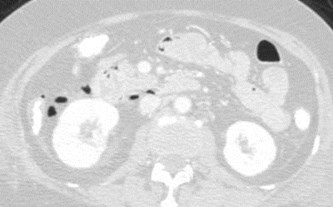
Acute epigastric pain
Perforated duodenal ulcer: air in anterior pararenalspace spreading to right perinephric space

Study of 8 patients with confirmed perforationin 2nd portion of duodenum
Air observed in right perirenal space in 88%
Theory: Variability in medial extension of rightARF responsible for location of air.
When ARF passed posterior to duodenum, fusingwith perivascular structures in central peritoneum,air did NOT enter perirenal space.
When ARF extended medially to 2nd portion ofduodenum air extended into right perirenal space.
Yasan. Radiology 2009


Collections related toureteroscopy: urinomas-hemorrhages
Subcapsular
Perinephric
Pararenal

Subcapsular collection
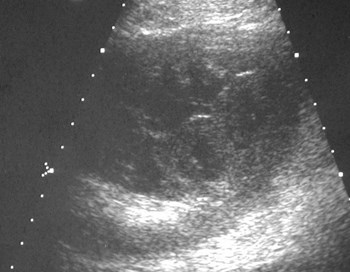
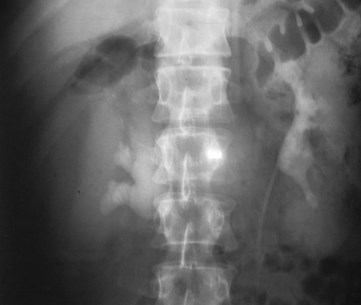

Perinephric Collection
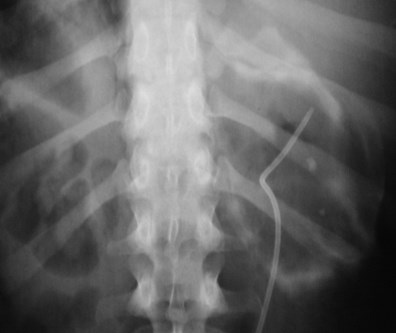

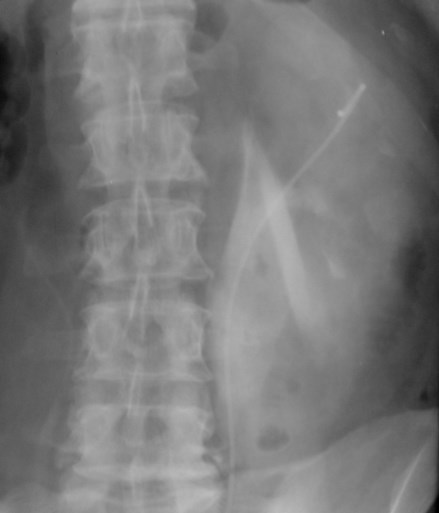

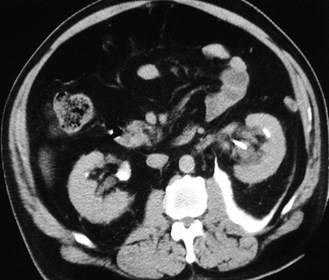
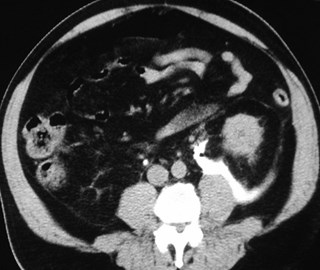
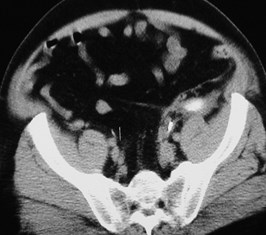
Posterior PararenalRegion- withinretrorenal space
Minor pathway into pelvis,lateral to iliac vessels

Hematomas
Traumatic- MVA, iatrogenic
Spontaneous- tumor, vascular(AAA, AVM, arteritis), hematologicdisorders, endstage kidney
Spread of hepatic or splenichematomas to perinephric spacewithout renal injury
Leaking aortic aneurysm

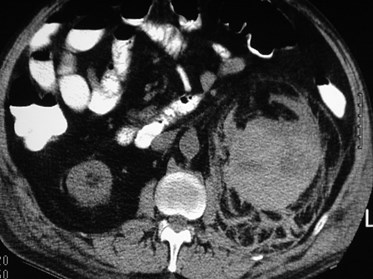
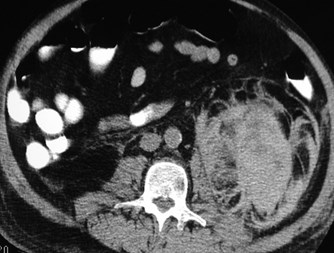
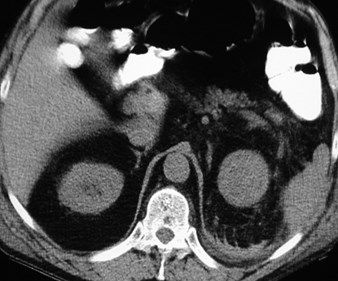
Renal Cell Carcinoma
with spontaneous
hemorrhage
SubcapsularBridgingSeptiPost pararenal space
Spread across midline belowlevel of renal hila

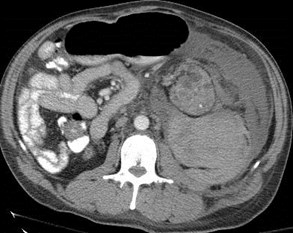
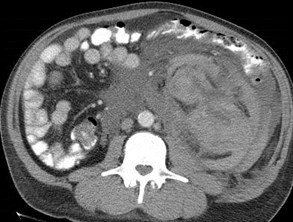
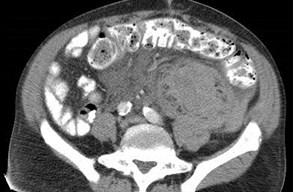
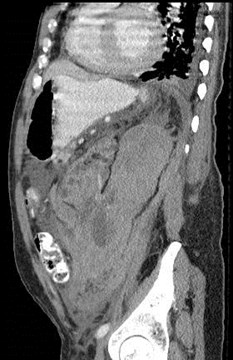
Endstage renal disease
Large spontaneoushemorrhage crossesmultiple boundaries

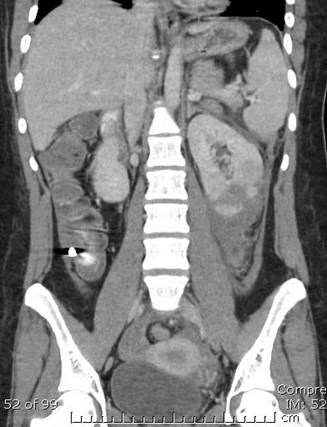
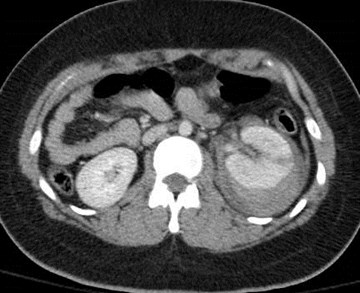
Blunt Trauma
Predominantly perinephric hematoma

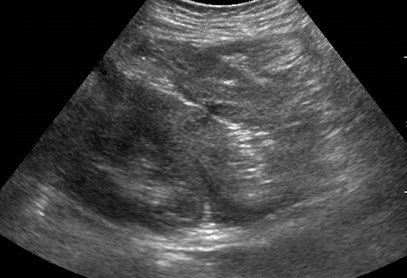
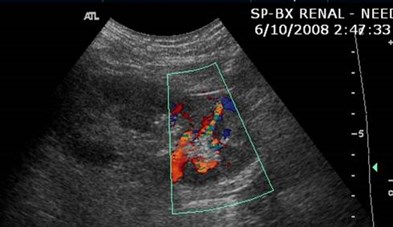
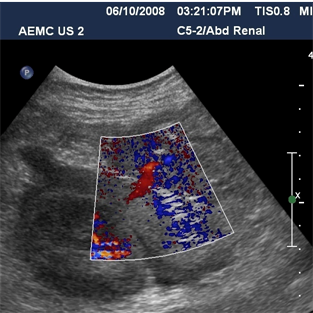
Immediate postbiopsy imaging
Acute perinephric and posterior pararenal hematomas

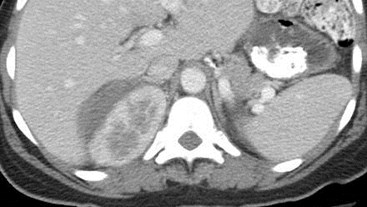
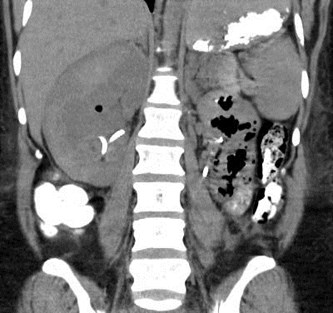
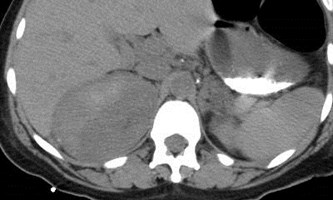
Pain after nephrostomy
Follow up
Subcapsularhematoma

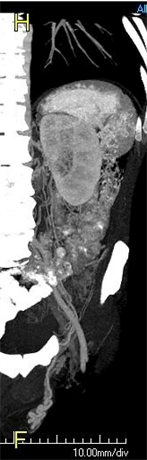
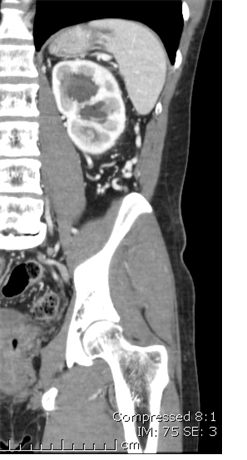
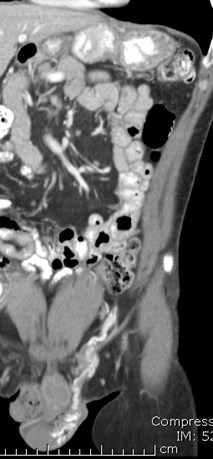
Retroperitoneal varices and varicocele
History of left renal vein thrombosis

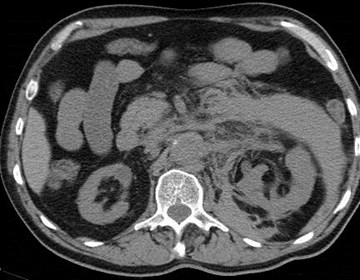
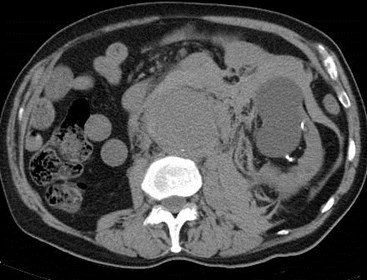
Acute pain and hypotension
Ruptured AAA predominantly involvinganterior and posterior pararenal spaces

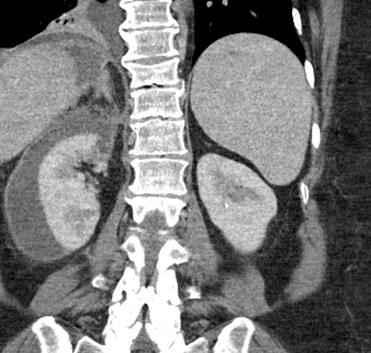
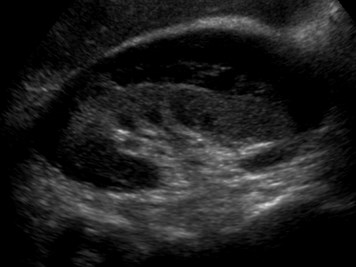
History of trauma
Perinephric Seroma

Acute ureteral calculi
Secondaryfindings include:
1. Thickening ofGerota’s fascia
2. Perinephric fluid
3. Renal enlargement
4. Delayed function
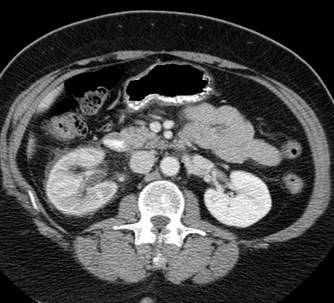

Solid Processes
Tumors
–Renal Cell Carcinoma
–Lymphoma-multiple or single renal masses,contiguous retroperitoneal masses, perirenalmasses
–Metastases-to perirenal lymphatics -melanoma, RCC, lung (via pleura/mediastinalconnections)
–Primary Retroperitoneal Tumors
Fibrosis-AO, IVC, ureters, perirenal space
Amyloidosis-perirenal soft tissue collections
Fat

Renal Cell Carcinoma
with spread through perirenal space toGerota’s Fascia
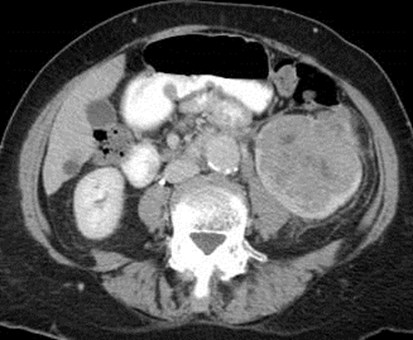

Retroperitoneal Lymphoma
Lymphadenopathy- can directlyinvade kidney or encase ureter
Perirenal involvement-transcapsular, direct spreadfrom lymph nodes, isolateddisease (least common)

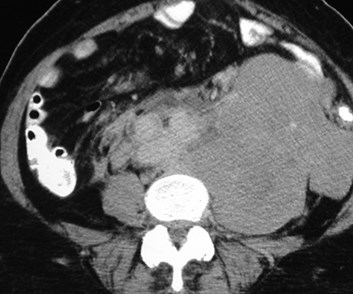
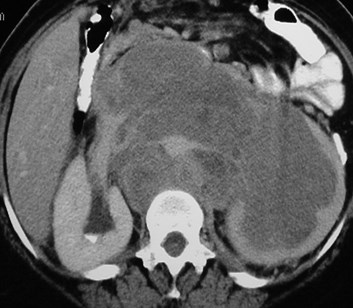
Lymphoma- Direct invasion of Kidneys
Small bowel mesentery anterior pararenal space renalhilum renal sinus, sparing perinephric space

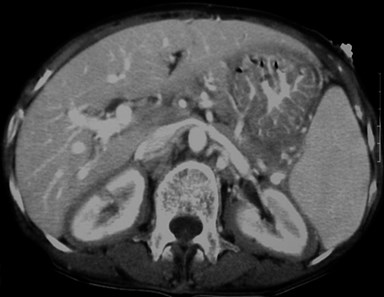
Bilateral Perirenal Lymphoma
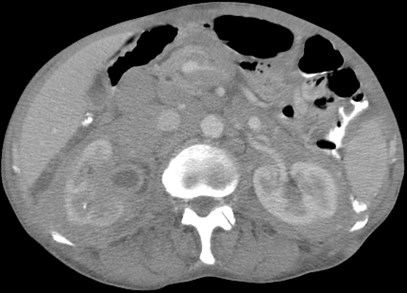
Two different patients

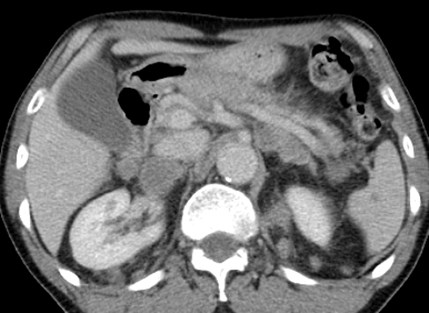
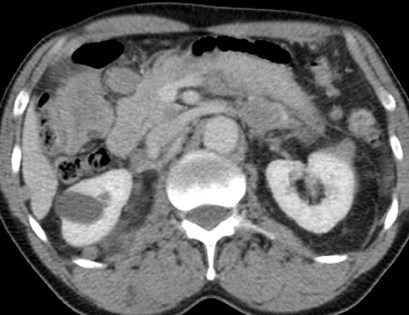
Within perinephric space, to Gerota’sfascia, adrenal glands
Metastatic Lung Cancer

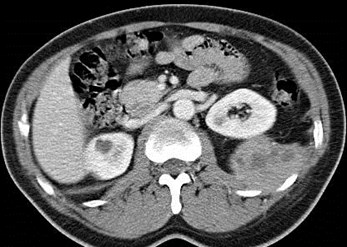
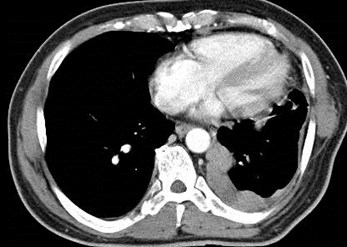
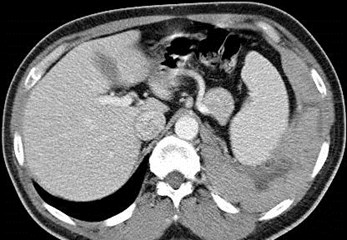
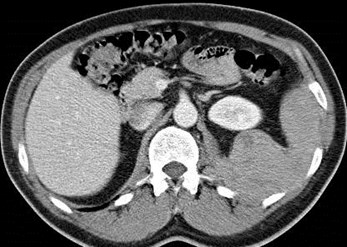
Malignant Thymoma
Extension from pleural space across diaphragm intoposterior pararenal space

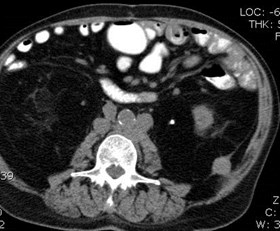
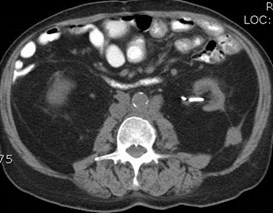
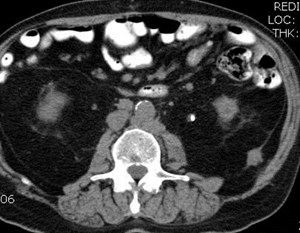
History of Prostate CA
3-05
10-05
7-06
9-06
Metastases to posterior pararenal fascia
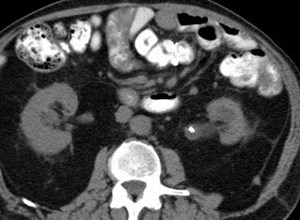

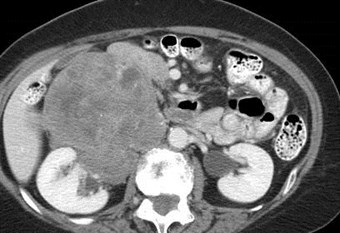
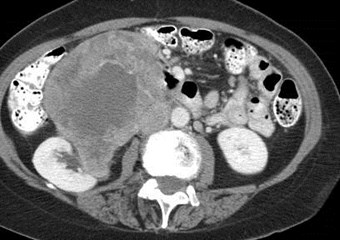
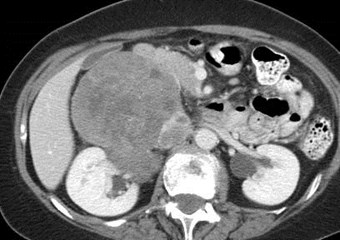
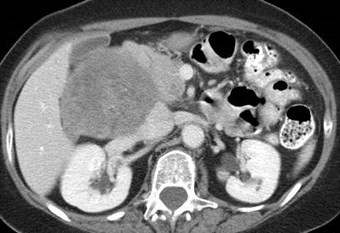
Sarcoma in right anterior pararenal spaceinvading IVC and perirenal space

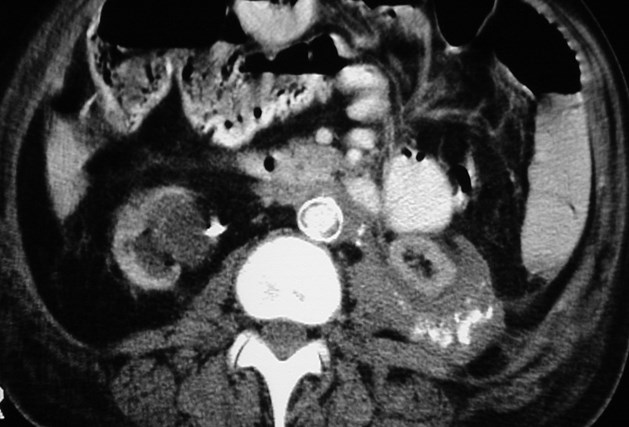
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis extending
into perinephric and postpararenal
spaces

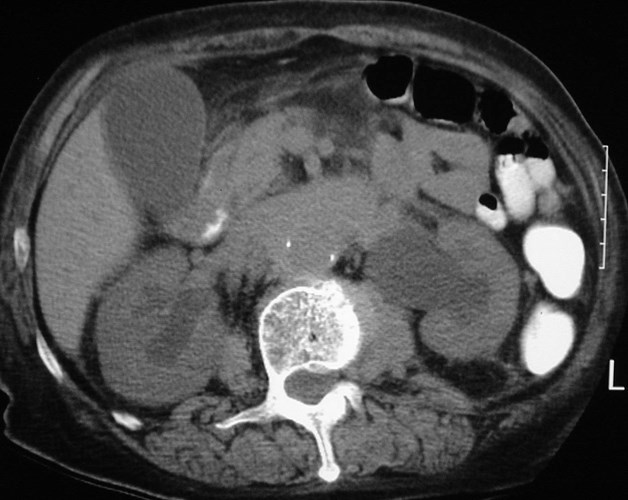
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis

Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Most commonly idiopathic
Other causes: aortic hemorrhage,aortitis, methysergide toxicity, priorsurgery or XRT, collagen vasculardisease (Riedel’s thyroiditis,sclerosing mediastinitis)
Clinical: 40-60 yrs, males>females
Hydronephrosis, ureteral narrowing,slight medial ureteral displacement

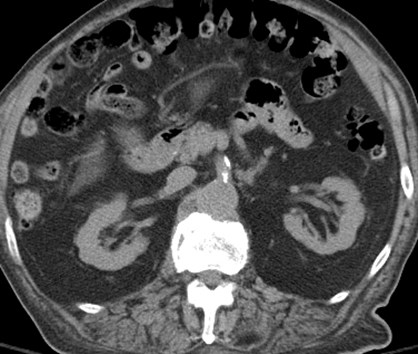
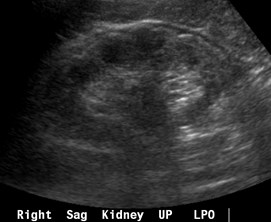
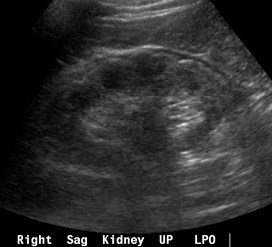
Prominent subcapsular fat
Miscellaneous

References
Aikawa, etal. Pelvic Extension of Retroperitoneal Fluid: Analysis inVivo. AJR 1998;671-677
Aizenstein, etal. Interfascial and Perinephric Pathways in theSpread of Retroperitoneal Disease: Refined Concepts Based on CTobservations. AJR 1997;168:639-643
Bechtold, etal. The Perirenal Space: Relationship of PathologicProcesses to Normal Retroperitoneal Anatomy. Radiographics1996;16:841-854
Molmenti, etal. Anatomy of the Retroperitoneum: Observations ofthe Distribution of Pathologic Fluid Collections. Radiology1996;200:95-103
Rastopoulous, etal. Medial Border of the Perirenal Space: CT andAnatomic Correlation. Radiology 1997;205:777-784
Thornton, etal. Helical CT Evaluation of the Perirenal Space and ItsBoundaries: A Cadaveric Study. Radiology 2001;659-663
Yasan, etal. Extension of Air into the Right Perirenal Space afterDuodenal Perforation: CT Findings. Radiology 2009;250:740

Mt. Shasta, northern California, summer 2012
